Auto Configuration in Spring boot
(The version referred for explanation in this article is Spring-boot 2.4.4)

While adding notes., I found this to be a vast topic, So I will cover the important things that will help to get a quick grip on the Auto-Configuration in spring boot
@SpringBootApplication annotation helps to Enable Autoconfiguration our classes by default.
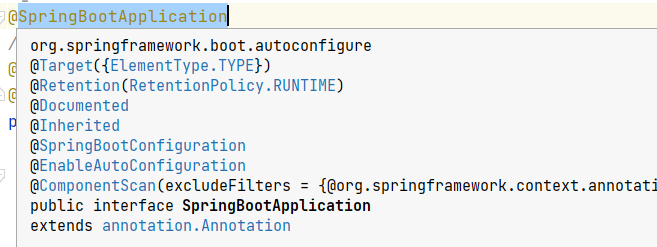
So our SpringBootApplication class makes the auto-configuration for us by incorporating the AutoConfiguration
AutoConfiguration-Basics
AutoConfiguration does the basic job of registering the user-defined beans and other bean data as Spring beans
The Spring beans which got generated are managed by the Spring IOC, which is helpful for the application execution
Inside an Autoconfiguration, We can find the intelligence of picking up the beans that could be possibly be needed for the application execution
Example
if I have a dependency of liquibase along with DB connection and if I exclude it from the AutoConfiguration mechanism by providing
@EnableAutoConfiguration(exclude={DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})During my application start, it will throw an error like
org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type ‘com.example.api.userdataoperatons.UserRepository’ available: expected at least 1 bean which qualifies as autowire candidate. Dependency annotations: {@org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired(required=true)}
So If you need your dependencies to be handled by the Spring Container itself, then we can be completely reliable on the intelligent Auto-Configuration
But wait, We still need a developer’s touch with Auto-Configuration
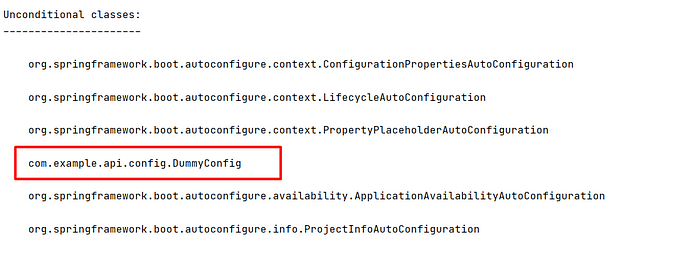
We’ll add the following code to get the classes that are registered as a part of the Auto-Configuration process
ApplicationContext a =SpringApplication.run(ApiApplication.class, args);
List<String> s = Arrays.asList(a.getBeanDefinitionNames().clone());
s.forEach(x->System.out.println(x));In the terminal, We will get the list of classes that are registered. Since Application Context contains all the functionalities of the beanFactory interface, we can get the registered class names
A little more debugging is required now., So in the VM-options give -Ddebug=true, then run the application now please see your terminal/console
It will give both positive and negative matches for the classes that have been registered in to the Spring context
For example
Positive case:
LiquibaseAutoConfiguration.LiquibaseEntityManagerFactoryDependsOnPostProcessor matched:
— @ConditionalOnClass found required class ‘org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean’ (OnClassCondition)
Negative case:
JsonbAutoConfiguration:
Did not match:
— @ConditionalOnClass did not find required class ‘javax.json.bind.Jsonb’ (OnClassCondition)
Maybe we need a much bigger and a newer article to go through the complete debugging
Annotate your class with @Configuration to get it registered as a Spring bean during our Application start

Some Articles that helped me to get a good knowledge of Auto-Configuration and Application-Context
https://www.baeldung.com/spring-boot-custom-auto-configuration
https://www.baeldung.com/spring-application-context
Happy Learning!!!!